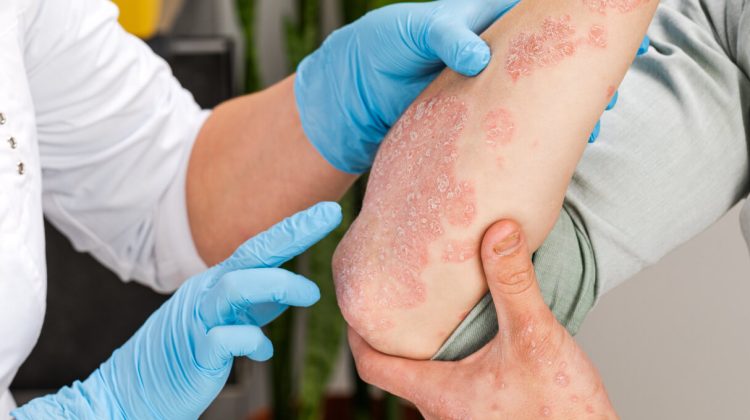
Psoriasis is more than just a skin condition—it’s a chronic inflammatory disease that can affect various parts of the body. For those living with psoriasis, managing chronic inflammation is a crucial aspect of maintaining overall health and well-being.
This guide will explore effective strategies for managing inflammation associated with psoriasis, from lifestyle changes to medical treatments, and provide answers to common questions about this condition.
Understanding Psoriasis and Chronic Inflammation
Psoriasis is an autoimmune condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, leading to the rapid buildup of skin cells and causing red, scaly patches on the skin. But psoriasis is not just skin-deep; it is also linked to chronic inflammation that can affect joints (psoriatic arthritis), the cardiovascular system, and other organs.
The Role of Chronic Inflammation
Inflammation is the body’s natural response to injury or infection, but in psoriasis, this response is overactive. The chronic inflammation associated with psoriasis doesn’t just affect the skin.
it can contribute to a range of comorbid conditions, including cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, and diabetes. Managing this inflammation is key to reducing symptoms and preventing further health complications.
Strategies for Managing Chronic Inflammation with Psoriasis
1. Adopt an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
Diet plays a significant role in managing inflammation. An anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids can help reduce inflammation. Foods such as fatty fish, leafy greens, berries, nuts, and seeds are particularly beneficial. Conversely, it’s advisable to avoid foods that can trigger inflammation, such as processed foods, red meats, and sugary beverages.
2. Incorporate Regular Exercise
Regular physical activity is another effective way to manage chronic inflammation. Exercise helps reduce inflammatory markers in the body and can also alleviate stress, which is a known trigger for psoriasis flare-ups. Low-impact activities like walking, swimming, and yoga are excellent choices for individuals with psoriasis.
3. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Obesity is a risk factor for increased inflammation, and individuals with psoriasis who are overweight may experience more severe symptoms. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can significantly reduce inflammation and improve psoriasis symptoms.
4. Use Topical and Systemic Treatments
Medical treatments play a crucial role in managing chronic inflammation in psoriasis. Topical treatments, such as corticosteroids and vitamin D analogs, can reduce inflammation and soothe skin symptoms. For more severe cases, systemic treatments like biologics and oral medications target the underlying inflammation and can help prevent flare-ups.
5. Manage Stress Effectively
Stress is a common trigger for psoriasis flare-ups, and managing stress is vital for controlling inflammation. Techniques such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, and progressive muscle relaxation can help reduce stress levels and, in turn, lower inflammation.
6. Monitor and Manage Comorbidities
Individuals with psoriasis are at a higher risk of developing comorbid conditions related to chronic inflammation, such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes. Regular monitoring and management of these conditions are essential to prevent further health complications. Working closely with healthcare providers to address these risks is crucial for overall health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Can diet alone control chronic inflammation in psoriasis?
Answer: While diet plays a significant role in managing chronic inflammation, it is often most effective when combined with other strategies such as regular exercise, stress management, and medical treatments. An anti-inflammatory diet can help reduce inflammation, but it should be part of a comprehensive approach to managing psoriasis.
Are there any specific foods that should be avoided to reduce inflammation in psoriasis?
Answer: Yes, certain foods can exacerbate inflammation in psoriasis. These include processed foods, red meat, refined sugars, and dairy products. It’s best to avoid or limit these foods while focusing on an anti-inflammatory diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats.
How effective are biologics in managing chronic inflammation in psoriasis?
Answer: Biologics are highly effective in managing chronic inflammation in moderate to severe cases of psoriasis. They work by targeting specific parts of the immune system responsible for inflammation, providing relief from symptoms and reducing the risk of associated comorbidities.
Can stress management techniques really help in reducing psoriasis flare-ups?
Answer: Absolutely. Stress is a known trigger for psoriasis flare-ups, and managing stress can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of these episodes. Techniques like mindfulness, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress effectively.
What role does weight management play in controlling psoriasis-related inflammation?
Answer: Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for controlling inflammation in psoriasis. Obesity increases the risk of severe psoriasis symptoms and associated comorbidities. Weight loss through diet and exercise can help reduce inflammation and improve overall health.
Conclusion
Managing chronic inflammation with psoriasis requires a multifaceted approach that includes lifestyle changes, medical treatments, and stress management. By adopting an anti-inflammatory diet, engaging in regular physical activity, managing weight, and using appropriate treatments, individuals with psoriasis can significantly reduce inflammation and improve their quality of life. If you’re looking for personalized advice or treatment options, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider.
For more detailed information on managing psoriasis and chronic inflammation, you can visit these trusted resources:
